|
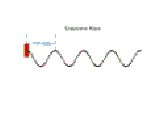
-
A wave is a
disturbance in a medium.
-
It carries energy from one
point to another without transferring matter.
-
There are two main types:
Longitudinal and Transverse.
-
Sound waves are an example
of longitudinal waves.
-
Typically, sound waves
travel at about 340 meters per second in air at room temperature and
pressure.
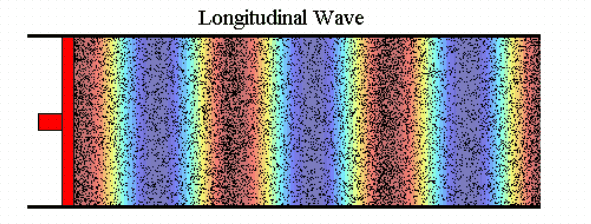
We use three ways of representing the propagation of waves:
-
Dots.
-
Colour maps.
-
Line graphs.
WAVELENGTH-FREQUENCY RELATION
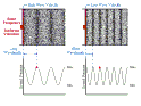
Frequency,
f, wavelength,
λ,
and wave velocity,
v, are
mathematically related by:
v =
f λ
POINT SOURCES, INVERSE SQUARE
LAW

The energy carried by waves
that radiate uniformly in all directions from a point source decay as the
inverse of the square of the distance from the point source. This is known
as the inverse square law.
|