Fluid Dynamics and Acoustics Group
|
VIRTUAL ACOUSTICS AND AUDIO
ENGINEERING Fluid Dynamics and Acoustics Group |
|
| | |
|
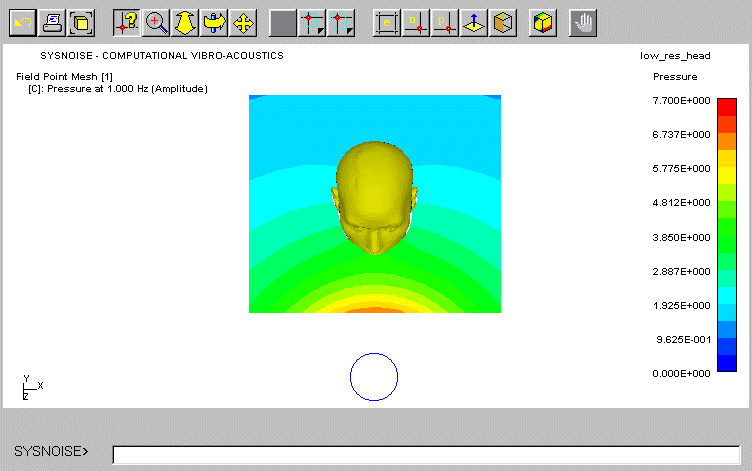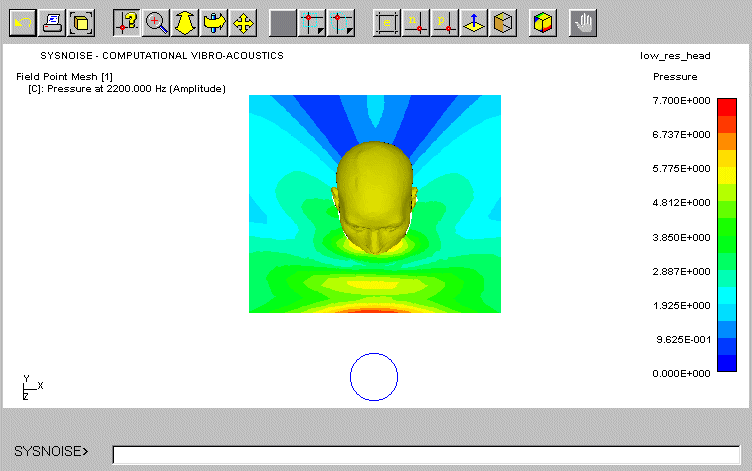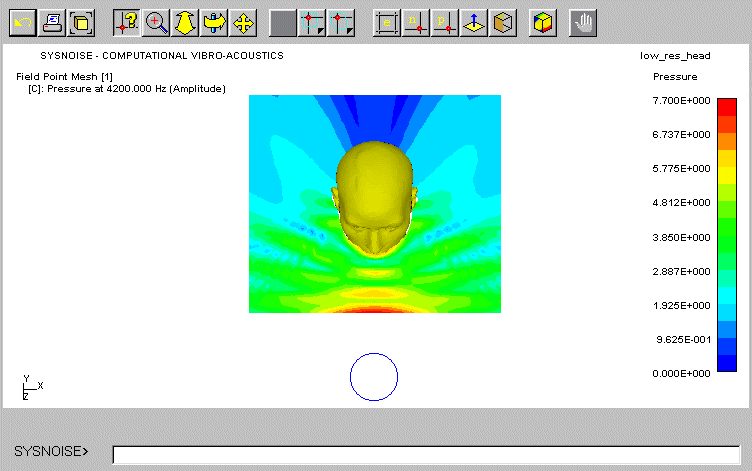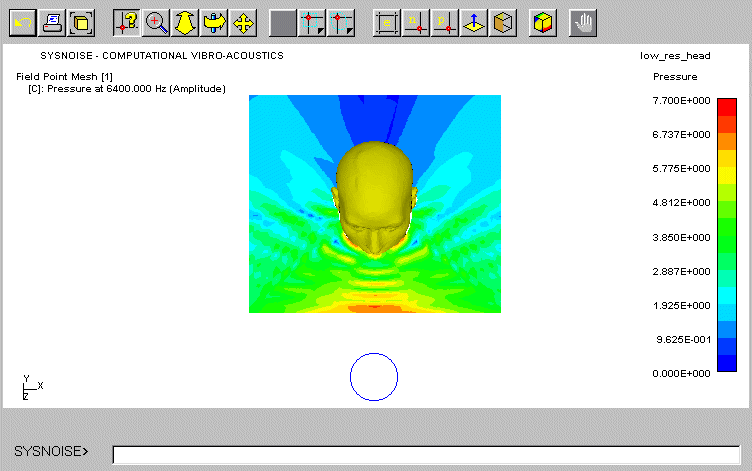
Frequency domain response with the DBEM When the human head is simplified
to the classical rigid sphere, analytical expressions exist for both the
frequency response on the sphere surface and also the total sound field
due to an excitation of a plane wave or a monopole source. However, it
was demonstrated that the pinna can produce a much more complex structure
of frequency response at high frequencies. An example of the sound field
around KEMAR (without a torso) calculated with the DBEM is shown. In this
case the mesh model of KEMAR included 10283 nodes and 20562 elements (of
a full head), and the mesh of the field points around the head comprises
of 200 × 200 points. The total (incident + scattered) sound pressure
in an area of 0.5 m x 0.5 m is shown on a linear scale. The source is positioned
in front of the head at a distance of 0.5 m from the centre of the head.
The characteristics of the sound fields are very similar to the case of
a sphere where at 200 Hz the head is almost transparent to the propagating
waves. At 1 kHz the shadow zones appear at the rear, and an increase of
pressure occurs in front of the head due to the superposition of the incident
and reflected waves. As frequency increases (at 2 kHz and 5 kHz), the interference
between these waves causes more complex patterns in front of the head and
higher attenuation is noticed at the rear. In addition, the scattered sound
field is slightly uneven on the left and right sides due probably to slight
misalignment and due to the asymmetrical shape of KEMAR mesh model with
DB60 and DB61 pinnae.
 |